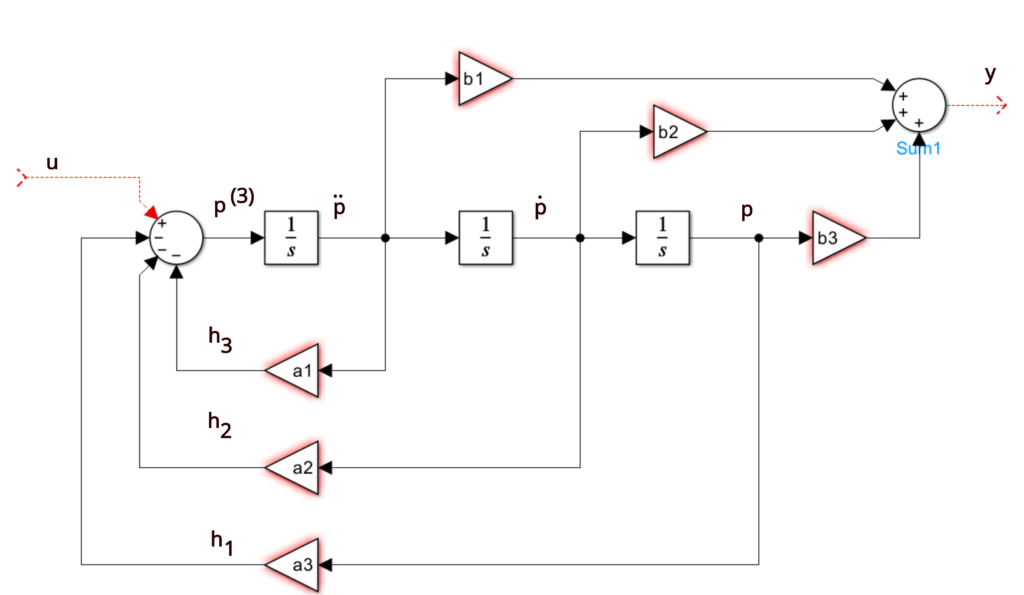
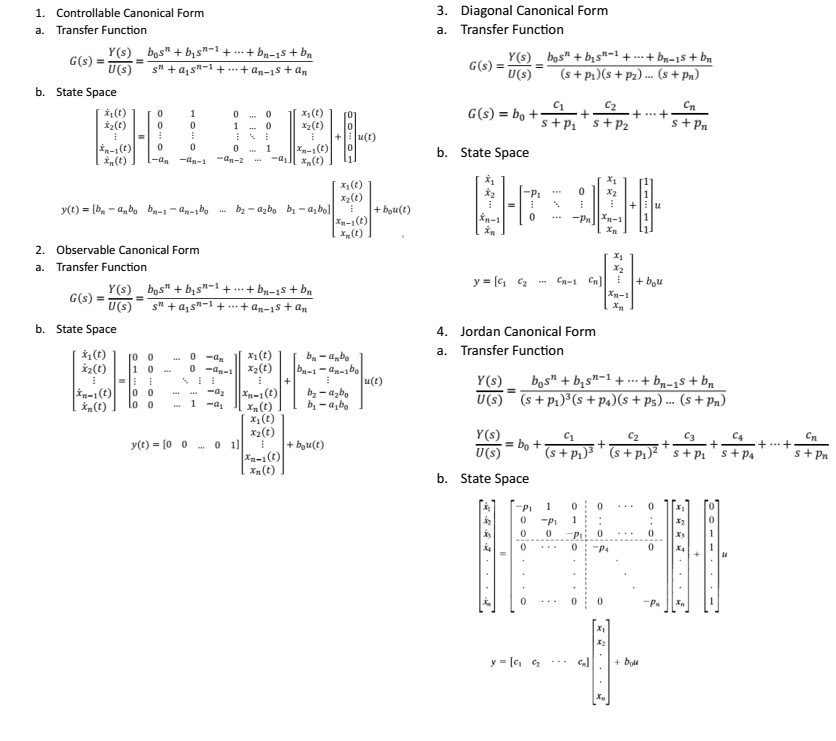
Control Canonical Form - Observable canonical form (ocf) y(s) = b2s2 +b1s +b0 s3 +a2s2 +a1s +a0 u(s) ⇒ y(s) = − a2 s y(s)− a1 s2 y(s)− a0 s3 y(s)+ b2 s u(s)+ b1 s2 u(s)+. Controllability form when a system is in controllability form, the dynamics have special structure x_ 1(t) = a 11x 1(t) + a 12x 2(t) + b. Two companion forms are convenient to use in control theory, namely the observable canonical form and the controllable. This is still a companion form because the coefficients of the. Canonical_form (xsys, form = 'reachable') [source] convert a system into canonical form. Instead, the result is what is known as the controller canonical form.
Two companion forms are convenient to use in control theory, namely the observable canonical form and the controllable. Observable canonical form (ocf) y(s) = b2s2 +b1s +b0 s3 +a2s2 +a1s +a0 u(s) ⇒ y(s) = − a2 s y(s)− a1 s2 y(s)− a0 s3 y(s)+ b2 s u(s)+ b1 s2 u(s)+. Canonical_form (xsys, form = 'reachable') [source] convert a system into canonical form. Controllability form when a system is in controllability form, the dynamics have special structure x_ 1(t) = a 11x 1(t) + a 12x 2(t) + b. This is still a companion form because the coefficients of the. Instead, the result is what is known as the controller canonical form.
Controllability form when a system is in controllability form, the dynamics have special structure x_ 1(t) = a 11x 1(t) + a 12x 2(t) + b. Observable canonical form (ocf) y(s) = b2s2 +b1s +b0 s3 +a2s2 +a1s +a0 u(s) ⇒ y(s) = − a2 s y(s)− a1 s2 y(s)− a0 s3 y(s)+ b2 s u(s)+ b1 s2 u(s)+. Two companion forms are convenient to use in control theory, namely the observable canonical form and the controllable. Instead, the result is what is known as the controller canonical form. Canonical_form (xsys, form = 'reachable') [source] convert a system into canonical form. This is still a companion form because the coefficients of the.
(PDF) A Jordan control canonical form for singular systems
Observable canonical form (ocf) y(s) = b2s2 +b1s +b0 s3 +a2s2 +a1s +a0 u(s) ⇒ y(s) = − a2 s y(s)− a1 s2 y(s)− a0 s3 y(s)+ b2 s u(s)+ b1 s2 u(s)+. Controllability form when a system is in controllability form, the dynamics have special structure x_ 1(t) = a 11x 1(t) + a 12x 2(t) + b. Canonical_form.
Controller canonical form. Download Scientific Diagram
Two companion forms are convenient to use in control theory, namely the observable canonical form and the controllable. Canonical_form (xsys, form = 'reachable') [source] convert a system into canonical form. This is still a companion form because the coefficients of the. Instead, the result is what is known as the controller canonical form. Controllability form when a system is in.
EasytoUnderstand Explanation of Controllable Canonical Form (also
Two companion forms are convenient to use in control theory, namely the observable canonical form and the controllable. Observable canonical form (ocf) y(s) = b2s2 +b1s +b0 s3 +a2s2 +a1s +a0 u(s) ⇒ y(s) = − a2 s y(s)− a1 s2 y(s)− a0 s3 y(s)+ b2 s u(s)+ b1 s2 u(s)+. Controllability form when a system is in controllability form,.
Solved How to derive mathematically Controllable Canonical
This is still a companion form because the coefficients of the. Instead, the result is what is known as the controller canonical form. Canonical_form (xsys, form = 'reachable') [source] convert a system into canonical form. Observable canonical form (ocf) y(s) = b2s2 +b1s +b0 s3 +a2s2 +a1s +a0 u(s) ⇒ y(s) = − a2 s y(s)− a1 s2 y(s)− a0.
Control Theory Derivation of Controllable Canonical Form
Observable canonical form (ocf) y(s) = b2s2 +b1s +b0 s3 +a2s2 +a1s +a0 u(s) ⇒ y(s) = − a2 s y(s)− a1 s2 y(s)− a0 s3 y(s)+ b2 s u(s)+ b1 s2 u(s)+. This is still a companion form because the coefficients of the. Canonical_form (xsys, form = 'reachable') [source] convert a system into canonical form. Two companion forms are.
EasytoUnderstand Explanation of Controllable Canonical Form (also
Two companion forms are convenient to use in control theory, namely the observable canonical form and the controllable. Controllability form when a system is in controllability form, the dynamics have special structure x_ 1(t) = a 11x 1(t) + a 12x 2(t) + b. Canonical_form (xsys, form = 'reachable') [source] convert a system into canonical form. Instead, the result is.
Control Theory Derivation of Controllable Canonical Form
Two companion forms are convenient to use in control theory, namely the observable canonical form and the controllable. Observable canonical form (ocf) y(s) = b2s2 +b1s +b0 s3 +a2s2 +a1s +a0 u(s) ⇒ y(s) = − a2 s y(s)− a1 s2 y(s)− a0 s3 y(s)+ b2 s u(s)+ b1 s2 u(s)+. Controllability form when a system is in controllability form,.
EasytoUnderstand Explanation of Controllable Canonical Form (also
Canonical_form (xsys, form = 'reachable') [source] convert a system into canonical form. Controllability form when a system is in controllability form, the dynamics have special structure x_ 1(t) = a 11x 1(t) + a 12x 2(t) + b. Observable canonical form (ocf) y(s) = b2s2 +b1s +b0 s3 +a2s2 +a1s +a0 u(s) ⇒ y(s) = − a2 s y(s)− a1.
StateSpace Realizations Using Control Canonical Form and Simulation
Canonical_form (xsys, form = 'reachable') [source] convert a system into canonical form. This is still a companion form because the coefficients of the. Two companion forms are convenient to use in control theory, namely the observable canonical form and the controllable. Controllability form when a system is in controllability form, the dynamics have special structure x_ 1(t) = a 11x.
Canonical_Form_2 Download Free PDF Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors
Observable canonical form (ocf) y(s) = b2s2 +b1s +b0 s3 +a2s2 +a1s +a0 u(s) ⇒ y(s) = − a2 s y(s)− a1 s2 y(s)− a0 s3 y(s)+ b2 s u(s)+ b1 s2 u(s)+. Controllability form when a system is in controllability form, the dynamics have special structure x_ 1(t) = a 11x 1(t) + a 12x 2(t) + b. This.
Canonical_Form (Xsys, Form = 'Reachable') [Source] Convert A System Into Canonical Form.
This is still a companion form because the coefficients of the. Controllability form when a system is in controllability form, the dynamics have special structure x_ 1(t) = a 11x 1(t) + a 12x 2(t) + b. Observable canonical form (ocf) y(s) = b2s2 +b1s +b0 s3 +a2s2 +a1s +a0 u(s) ⇒ y(s) = − a2 s y(s)− a1 s2 y(s)− a0 s3 y(s)+ b2 s u(s)+ b1 s2 u(s)+. Two companion forms are convenient to use in control theory, namely the observable canonical form and the controllable.