Glucose Forms A Cyclic Hemiacetal - The size of the cyclic hemiacetal ring adopted by a given sugar is not constant, but may vary with. Intramolecular hemiacetal formation is common in sugar chemistry. The first carbon atom (c1), which is an aldehyde. Most simple carbohydrates exist predominantly as cyclic hemiacetals. The sugar fructose is an isomer of glucose. Like glucose, fructose forms a cyclic hemiacetal,.
The first carbon atom (c1), which is an aldehyde. Intramolecular hemiacetal formation is common in sugar chemistry. Like glucose, fructose forms a cyclic hemiacetal,. The sugar fructose is an isomer of glucose. Most simple carbohydrates exist predominantly as cyclic hemiacetals. The size of the cyclic hemiacetal ring adopted by a given sugar is not constant, but may vary with.
The sugar fructose is an isomer of glucose. The size of the cyclic hemiacetal ring adopted by a given sugar is not constant, but may vary with. Like glucose, fructose forms a cyclic hemiacetal,. Most simple carbohydrates exist predominantly as cyclic hemiacetals. Intramolecular hemiacetal formation is common in sugar chemistry. The first carbon atom (c1), which is an aldehyde.
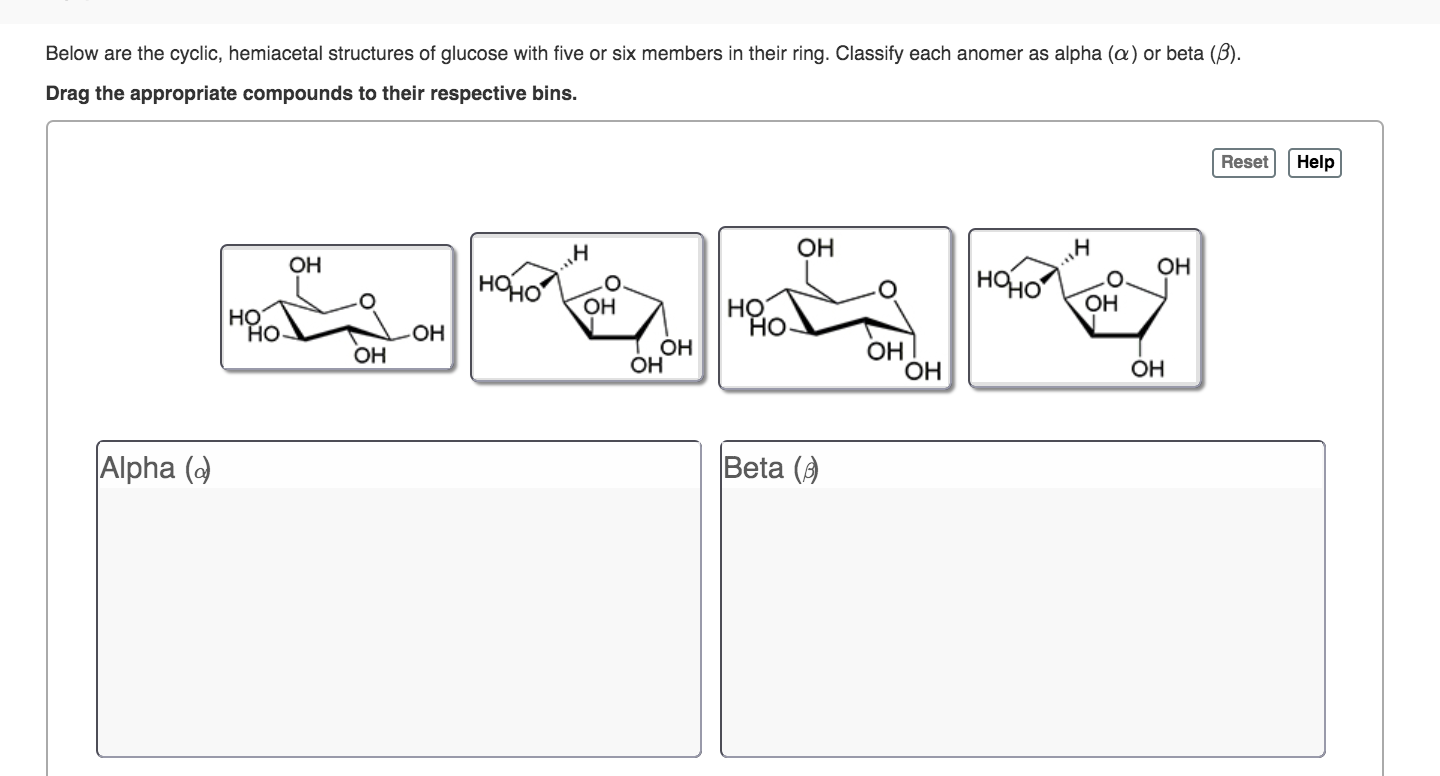
Solved Below are the cyclic, hemiacetal structures of
The size of the cyclic hemiacetal ring adopted by a given sugar is not constant, but may vary with. Like glucose, fructose forms a cyclic hemiacetal,. The first carbon atom (c1), which is an aldehyde. The sugar fructose is an isomer of glucose. Intramolecular hemiacetal formation is common in sugar chemistry.
Solved 9 When glucose forms a hemiacetal a) It
The sugar fructose is an isomer of glucose. The size of the cyclic hemiacetal ring adopted by a given sugar is not constant, but may vary with. The first carbon atom (c1), which is an aldehyde. Intramolecular hemiacetal formation is common in sugar chemistry. Most simple carbohydrates exist predominantly as cyclic hemiacetals.
Solved Glucose Generally Exists Greater Than 99 In The C...
Intramolecular hemiacetal formation is common in sugar chemistry. Most simple carbohydrates exist predominantly as cyclic hemiacetals. The sugar fructose is an isomer of glucose. The size of the cyclic hemiacetal ring adopted by a given sugar is not constant, but may vary with. Like glucose, fructose forms a cyclic hemiacetal,.
SOLVEDGlucose forms a cyclic hemiacetal in order to to prevent
Like glucose, fructose forms a cyclic hemiacetal,. The size of the cyclic hemiacetal ring adopted by a given sugar is not constant, but may vary with. Most simple carbohydrates exist predominantly as cyclic hemiacetals. The sugar fructose is an isomer of glucose. Intramolecular hemiacetal formation is common in sugar chemistry.
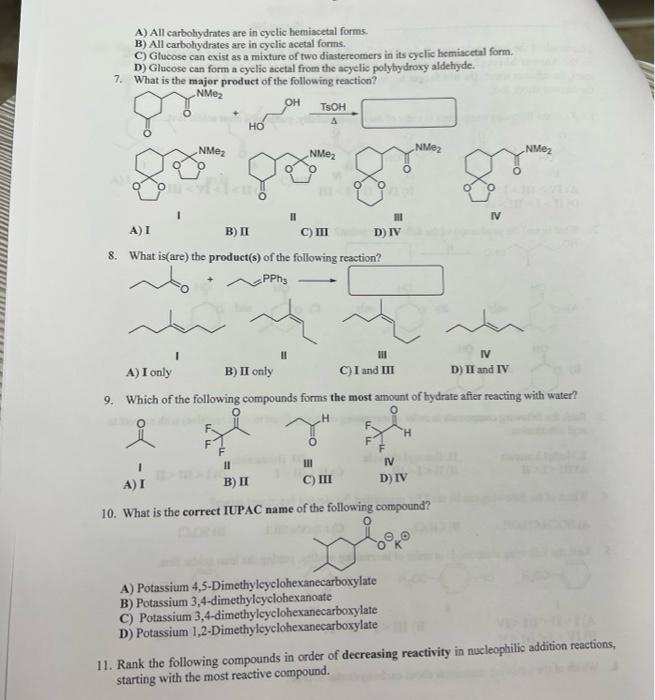
Solved A) All carbohydrates are in cyclic hemiacetal forms.
The sugar fructose is an isomer of glucose. Like glucose, fructose forms a cyclic hemiacetal,. Most simple carbohydrates exist predominantly as cyclic hemiacetals. Intramolecular hemiacetal formation is common in sugar chemistry. The size of the cyclic hemiacetal ring adopted by a given sugar is not constant, but may vary with.
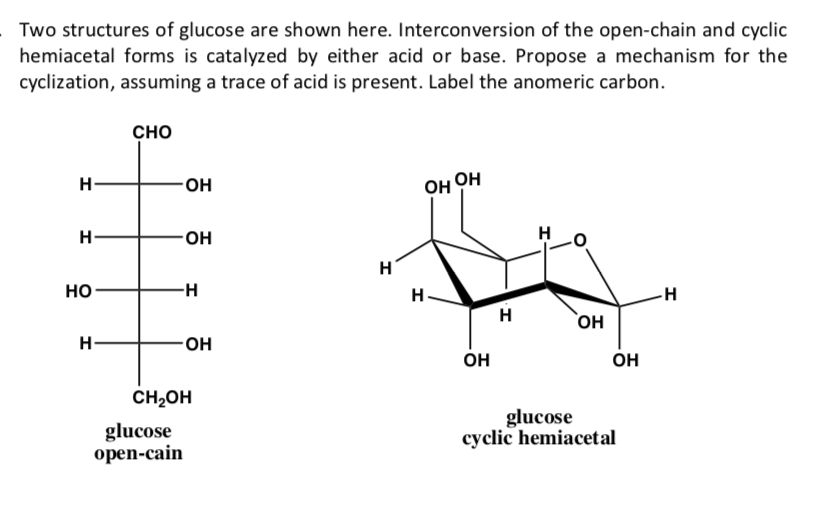
Solved Two structures of glucose are shown here.
Intramolecular hemiacetal formation is common in sugar chemistry. Like glucose, fructose forms a cyclic hemiacetal,. The first carbon atom (c1), which is an aldehyde. The size of the cyclic hemiacetal ring adopted by a given sugar is not constant, but may vary with. Most simple carbohydrates exist predominantly as cyclic hemiacetals.
SOLVED Carbohydrates cyclic , hemiacetal form with the OH on carbon
Intramolecular hemiacetal formation is common in sugar chemistry. Like glucose, fructose forms a cyclic hemiacetal,. The size of the cyclic hemiacetal ring adopted by a given sugar is not constant, but may vary with. Most simple carbohydrates exist predominantly as cyclic hemiacetals. The sugar fructose is an isomer of glucose.
Assertion Glucose does not give 2,4 DNP test.Reason Glucose exists in
The size of the cyclic hemiacetal ring adopted by a given sugar is not constant, but may vary with. Most simple carbohydrates exist predominantly as cyclic hemiacetals. Intramolecular hemiacetal formation is common in sugar chemistry. Like glucose, fructose forms a cyclic hemiacetal,. The first carbon atom (c1), which is an aldehyde.
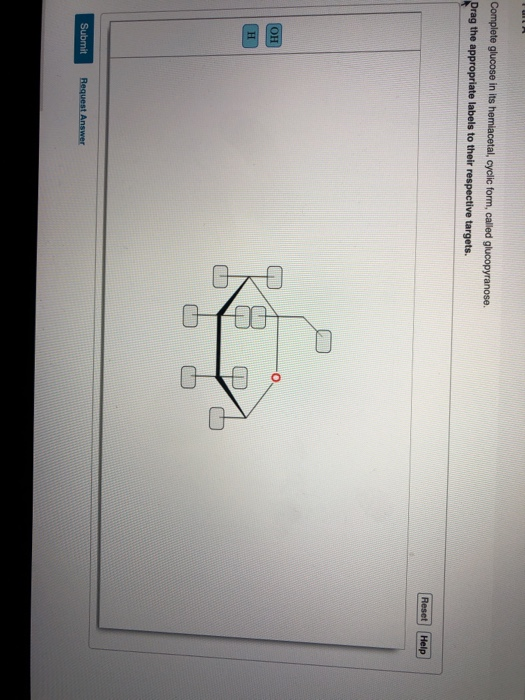
Solved Complete glucose in its hemiacetal, cyclic form,
Intramolecular hemiacetal formation is common in sugar chemistry. Like glucose, fructose forms a cyclic hemiacetal,. The first carbon atom (c1), which is an aldehyde. The size of the cyclic hemiacetal ring adopted by a given sugar is not constant, but may vary with. The sugar fructose is an isomer of glucose.
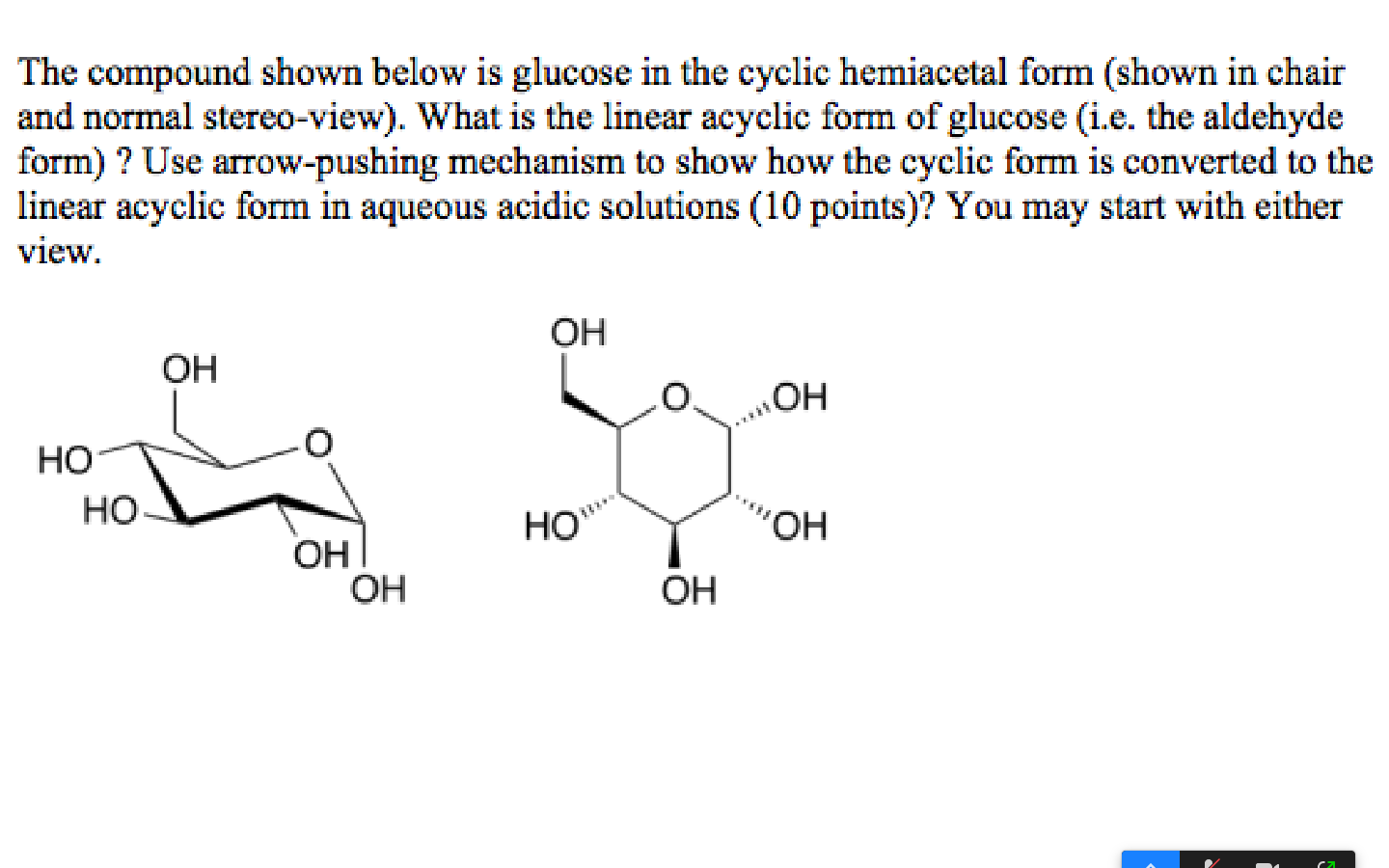
Solved The compound shown below is glucose in the cyclic
Like glucose, fructose forms a cyclic hemiacetal,. The size of the cyclic hemiacetal ring adopted by a given sugar is not constant, but may vary with. The first carbon atom (c1), which is an aldehyde. Intramolecular hemiacetal formation is common in sugar chemistry. The sugar fructose is an isomer of glucose.
The Size Of The Cyclic Hemiacetal Ring Adopted By A Given Sugar Is Not Constant, But May Vary With.
The first carbon atom (c1), which is an aldehyde. The sugar fructose is an isomer of glucose. Intramolecular hemiacetal formation is common in sugar chemistry. Most simple carbohydrates exist predominantly as cyclic hemiacetals.